Data Mining Camp - Biomedical Session
Posted by Patricia Hoffman on Wednesday, March 31, 2010
Notes from the Biomedical Data Mining Camp Session lead by Dr. Irene Gabashvili can be found at
http://aurametrix.blogspot.com/2010/03/health-data-self-service-visualization.html
Health Data, Self-serve, Visualization, Semantic Analysis and Collective Intelligence
Notes from the Biomedical Data Mining Camp Session led by Dr. Irene Gabashvili and other health-related discussions at Data Mining Camp and Transparency Camp 2010.
The title for the session was "Biomedical Data Mining: Successes, Failures, and Challenges" (streamedonline from Fireside C).
The topic stemmed from the similarly named last year's session - Biomedical Data Mining: Dimensionality, Noise, Applications - now split into several discussions including Bioinformatics & Genome Sequencing organized by Raymond McCauley, Dimensionality Reduction moderated by Luca Rigazio (HLDA / HDA; LDPP; Core Vector Machines; Sparse Proj SQ; Random Projection and Feature Selection).
Main sub-topics of the biomedical session were: 0 emerging technologies that could change the world". This is not only about mining data pertaining to social behavior - although social factors do impact well-being and social data provides valuable health predictors. It's also about health data collected in real and near real time. Audience asked about ways to collect health data and their limitations. Some of the questions reflected earlier Q&A with the Data Mining Camp expert panel , especially Dr. Michael Walker,author of numerous FDA and CLIA-approved products to diagnose and treat disease. He commented on the need to have tools well beyond the data available to take cell samples every two minutes instead of laboratory testing every few months - in order to allow cellular simulations and obtain parameters for differential equations. Sampling frequencies don't come close to allow this kind of modeling. Irene Gabashvili agreed that first-principles cellular modeling for predicting health won't be possible (although there are engineers that believe a platform for real-time in-vivo measurements of most cells can be developed). Yet, good predictors could be and will be developed - based on sensors measuring macro-level observations and missing value estimators. Genetic information is not enough, we need to capture environmental risk factors. How can we separate genes and environment?, asked one of the participants. Aurametrix' initial focus is on chemicals in our food - and even though some may argue that our taste and satiety mechanisms are dictated by genes, food analytics provides insights into non-genetic components of our health. Other questions were on the time line for body sensor networks and data growth. Jeffrey Nick of EMC estimates that personal sensor data will balloon from 10% of all stored information to 90% within the next decade. Irene Gabashvili thinks that this will happen rather sooner than later, perhaps in the next two years.
0 emerging technologies that could change the world". This is not only about mining data pertaining to social behavior - although social factors do impact well-being and social data provides valuable health predictors. It's also about health data collected in real and near real time. Audience asked about ways to collect health data and their limitations. Some of the questions reflected earlier Q&A with the Data Mining Camp expert panel , especially Dr. Michael Walker,author of numerous FDA and CLIA-approved products to diagnose and treat disease. He commented on the need to have tools well beyond the data available to take cell samples every two minutes instead of laboratory testing every few months - in order to allow cellular simulations and obtain parameters for differential equations. Sampling frequencies don't come close to allow this kind of modeling. Irene Gabashvili agreed that first-principles cellular modeling for predicting health won't be possible (although there are engineers that believe a platform for real-time in-vivo measurements of most cells can be developed). Yet, good predictors could be and will be developed - based on sensors measuring macro-level observations and missing value estimators. Genetic information is not enough, we need to capture environmental risk factors. How can we separate genes and environment?, asked one of the participants. Aurametrix' initial focus is on chemicals in our food - and even though some may argue that our taste and satiety mechanisms are dictated by genes, food analytics provides insights into non-genetic components of our health. Other questions were on the time line for body sensor networks and data growth. Jeffrey Nick of EMC estimates that personal sensor data will balloon from 10% of all stored information to 90% within the next decade. Irene Gabashvili thinks that this will happen rather sooner than later, perhaps in the next two years.
Another interesting aspect of reality mining is crowdsourcing or collective intelligence - in order to get useful information from all the data (temporospatial location, GPS, activity, food, symptoms, behavior, communication content, proximity sensing), we need to analyze it not only on individual but also group level. We need to share more, without sacrificing privacy and security. Collective contributions can be reliable - Shamod Lacoui's answer to this is in selecting those who contribute, restricting inputs to domain. It would help to “filter out the dross”, while “saving the best”. It is needed to suppress noise, to infer intelligence from the collection of facts, clicks, steps, whatever one can contribute. This resonates with discussions at the Transparency Camp - one of the useful tools isSwiftRiver - free, open source software platform to validate and filter news. Swift relies on Natural Language Processing, Machine Learning and Veracity Algorithms to track and verify the accuracy of reports and suppress noise (like duplicate content, irrelevant cross-chatter and inaccuracies). Transparency Camp also posed a question on whether there is a need for an FDA-like institution toensure information safety and healthy information consumption.
Self-serve was a topic of a smaller Data Mining Camp Session. Even though it was aimed at sales reps that need to go beyond Excel spreadsheets to mine private data of their interest, self-service is currently the only option for health care consumers. People need to analyze everyday life for health implications. They need better tools to not focus on metrics that are easy to collect instead of metrics we need to collect.
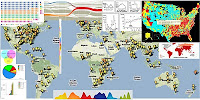 wledge from health data. Remember who invented the pie chart? That's right, it was Florence Nightingale, a nurse who needed a way to better represent her data. one of the most famous examples of visualizing epidemiological data was Dr. John Snow's map of deaths from a cholera outbreak in London, Many other techniques and software tools exist, but maps remain popular - especially google maps API. One of popular tools for epidemiological data is Google Maps API. For example, it embeds Google Maps into healthmap.org with JavaScript.
wledge from health data. Remember who invented the pie chart? That's right, it was Florence Nightingale, a nurse who needed a way to better represent her data. one of the most famous examples of visualizing epidemiological data was Dr. John Snow's map of deaths from a cholera outbreak in London, Many other techniques and software tools exist, but maps remain popular - especially google maps API. One of popular tools for epidemiological data is Google Maps API. For example, it embeds Google Maps into healthmap.org with JavaScript.
One of the participants of Biomedical Session developed kidsdata.org (@kidsdata on twitter). It provides insights into geospatial autism statistics and visualizes trends and other useful health-related information.
Another way to display geospatial data is Dynamic Choropleth Maps. Complex networks can be also explored with alluvial diagrams and other approaches. More visualization techniques and tools can be applied to health data - to look at the data in new ways and gain useful insights.
Some of the questions from the audience were on the availability of data. Sources discussed included CDC (see, for example, NHANES laboratory files; eHealth metrics) and Entrez Life Sciences databases.
Signal Detection and Signal Processing for Mining Information was another discussion topic.
Questions were on data mining versus simple tracking and signal monitoring. It was agreed that data mining is the key to health management. Cardionet, body sensors (see posts on teletracking, M-health,Telemedicine: part 1; Telemedicine: part 2; Health 2.0 Software tools, Devices to keep you healthy), SNP detection, telemedicine applications, random and rare electrocardiographic events and other applications were also discussed.
The title for the session was "Biomedical Data Mining: Successes, Failures, and Challenges" (streamedonline from Fireside C).
The topic stemmed from the similarly named last year's session - Biomedical Data Mining: Dimensionality, Noise, Applications - now split into several discussions including Bioinformatics & Genome Sequencing organized by Raymond McCauley, Dimensionality Reduction moderated by Luca Rigazio (HLDA / HDA; LDPP; Core Vector Machines; Sparse Proj SQ; Random Projection and Feature Selection).
Main sub-topics of the biomedical session were:
- Reality Mining
- Visualization
- Imaging
- Signal Processing
 0 emerging technologies that could change the world". This is not only about mining data pertaining to social behavior - although social factors do impact well-being and social data provides valuable health predictors. It's also about health data collected in real and near real time. Audience asked about ways to collect health data and their limitations. Some of the questions reflected earlier Q&A with the Data Mining Camp expert panel , especially Dr. Michael Walker,author of numerous FDA and CLIA-approved products to diagnose and treat disease. He commented on the need to have tools well beyond the data available to take cell samples every two minutes instead of laboratory testing every few months - in order to allow cellular simulations and obtain parameters for differential equations. Sampling frequencies don't come close to allow this kind of modeling. Irene Gabashvili agreed that first-principles cellular modeling for predicting health won't be possible (although there are engineers that believe a platform for real-time in-vivo measurements of most cells can be developed). Yet, good predictors could be and will be developed - based on sensors measuring macro-level observations and missing value estimators. Genetic information is not enough, we need to capture environmental risk factors. How can we separate genes and environment?, asked one of the participants. Aurametrix' initial focus is on chemicals in our food - and even though some may argue that our taste and satiety mechanisms are dictated by genes, food analytics provides insights into non-genetic components of our health. Other questions were on the time line for body sensor networks and data growth. Jeffrey Nick of EMC estimates that personal sensor data will balloon from 10% of all stored information to 90% within the next decade. Irene Gabashvili thinks that this will happen rather sooner than later, perhaps in the next two years.
0 emerging technologies that could change the world". This is not only about mining data pertaining to social behavior - although social factors do impact well-being and social data provides valuable health predictors. It's also about health data collected in real and near real time. Audience asked about ways to collect health data and their limitations. Some of the questions reflected earlier Q&A with the Data Mining Camp expert panel , especially Dr. Michael Walker,author of numerous FDA and CLIA-approved products to diagnose and treat disease. He commented on the need to have tools well beyond the data available to take cell samples every two minutes instead of laboratory testing every few months - in order to allow cellular simulations and obtain parameters for differential equations. Sampling frequencies don't come close to allow this kind of modeling. Irene Gabashvili agreed that first-principles cellular modeling for predicting health won't be possible (although there are engineers that believe a platform for real-time in-vivo measurements of most cells can be developed). Yet, good predictors could be and will be developed - based on sensors measuring macro-level observations and missing value estimators. Genetic information is not enough, we need to capture environmental risk factors. How can we separate genes and environment?, asked one of the participants. Aurametrix' initial focus is on chemicals in our food - and even though some may argue that our taste and satiety mechanisms are dictated by genes, food analytics provides insights into non-genetic components of our health. Other questions were on the time line for body sensor networks and data growth. Jeffrey Nick of EMC estimates that personal sensor data will balloon from 10% of all stored information to 90% within the next decade. Irene Gabashvili thinks that this will happen rather sooner than later, perhaps in the next two years.Another interesting aspect of reality mining is crowdsourcing or collective intelligence - in order to get useful information from all the data (temporospatial location, GPS, activity, food, symptoms, behavior, communication content, proximity sensing), we need to analyze it not only on individual but also group level. We need to share more, without sacrificing privacy and security. Collective contributions can be reliable - Shamod Lacoui's answer to this is in selecting those who contribute, restricting inputs to domain. It would help to “filter out the dross”, while “saving the best”. It is needed to suppress noise, to infer intelligence from the collection of facts, clicks, steps, whatever one can contribute. This resonates with discussions at the Transparency Camp - one of the useful tools isSwiftRiver - free, open source software platform to validate and filter news. Swift relies on Natural Language Processing, Machine Learning and Veracity Algorithms to track and verify the accuracy of reports and suppress noise (like duplicate content, irrelevant cross-chatter and inaccuracies). Transparency Camp also posed a question on whether there is a need for an FDA-like institution toensure information safety and healthy information consumption.
Self-serve was a topic of a smaller Data Mining Camp Session. Even though it was aimed at sales reps that need to go beyond Excel spreadsheets to mine private data of their interest, self-service is currently the only option for health care consumers. People need to analyze everyday life for health implications. They need better tools to not focus on metrics that are easy to collect instead of metrics we need to collect.
In order to mine high-dimensional health space, many disparate types of data should be mashed and validated, 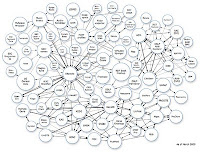 gaps should be bridged and structured metadata added to data.Randy Kerber talked about data formats and approaches to make it happen. Semantic web discussions involved NoSQL experts that mentioned limitations of gaining popularity technologies such as MongoDB, Cassandra and HBase. Another relevant session - on cloud computing - discussed its (sometimes over-rated ?) performance and Hadoop technologies.
gaps should be bridged and structured metadata added to data.Randy Kerber talked about data formats and approaches to make it happen. Semantic web discussions involved NoSQL experts that mentioned limitations of gaining popularity technologies such as MongoDB, Cassandra and HBase. Another relevant session - on cloud computing - discussed its (sometimes over-rated ?) performance and Hadoop technologies.
 wledge from health data. Remember who invented the pie chart? That's right, it was Florence Nightingale, a nurse who needed a way to better represent her data. one of the most famous examples of visualizing epidemiological data was Dr. John Snow's map of deaths from a cholera outbreak in London, Many other techniques and software tools exist, but maps remain popular - especially google maps API. One of popular tools for epidemiological data is Google Maps API. For example, it embeds Google Maps into healthmap.org with JavaScript.
wledge from health data. Remember who invented the pie chart? That's right, it was Florence Nightingale, a nurse who needed a way to better represent her data. one of the most famous examples of visualizing epidemiological data was Dr. John Snow's map of deaths from a cholera outbreak in London, Many other techniques and software tools exist, but maps remain popular - especially google maps API. One of popular tools for epidemiological data is Google Maps API. For example, it embeds Google Maps into healthmap.org with JavaScript.One of the participants of Biomedical Session developed kidsdata.org (@kidsdata on twitter). It provides insights into geospatial autism statistics and visualizes trends and other useful health-related information.
Another way to display geospatial data is Dynamic Choropleth Maps. Complex networks can be also explored with alluvial diagrams and other approaches. More visualization techniques and tools can be applied to health data - to look at the data in new ways and gain useful insights.
Some of the questions from the audience were on the availability of data. Sources discussed included CDC (see, for example, NHANES laboratory files; eHealth metrics) and Entrez Life Sciences databases.
Signal Detection and Signal Processing for Mining Information was another discussion topic.
Questions were on data mining versus simple tracking and signal monitoring. It was agreed that data mining is the key to health management. Cardionet, body sensors (see posts on teletracking, M-health,Telemedicine: part 1; Telemedicine: part 2; Health 2.0 Software tools, Devices to keep you healthy), SNP detection, telemedicine applications, random and rare electrocardiographic events and other applications were also discussed.
Tags: "biomedical" "visualization" "dimensionality reduction" "aurametrix" "croud sourcing" "collective intelligence"

Irene Gabashvili says For those who can't attend in person, watch live streaming or stream your live video by RSVP'ing at http://vokle.com/events/1547 (biomedical data mining) and http://vokle.com/events/1728 (other live & on-demand topics). Vote for topics or add your own at: http://urtak.com/u/719